Motivation 🌌 🌠
Recently I worked on a MeteorJS project. The live version of the app is hosted on Galaxy and there was no staging environment for this one. So we needed to deploy another instance of this app in a staging environment. The codebase was hosted on GitLab and we have a shared cluster of MongoDB in mLab. While we wanted to run the staging environment efficiently, we also wanted to make sure the deployment is as cost-effective as we can.
Finding 🆓 options
While searching for free options, I have found these best possible options:
- Heroku is one of the most used PaaS currently which supports deploying app automatically from the GitHub repository. However, deploying from other code repositories like GitLab, Bitbucket etc aren’t supported yet.
At the time of this writing, they support 4 different deployment methods:
These are: Heroku repo (GIT), GitHub, Dropbox, and Container Registry
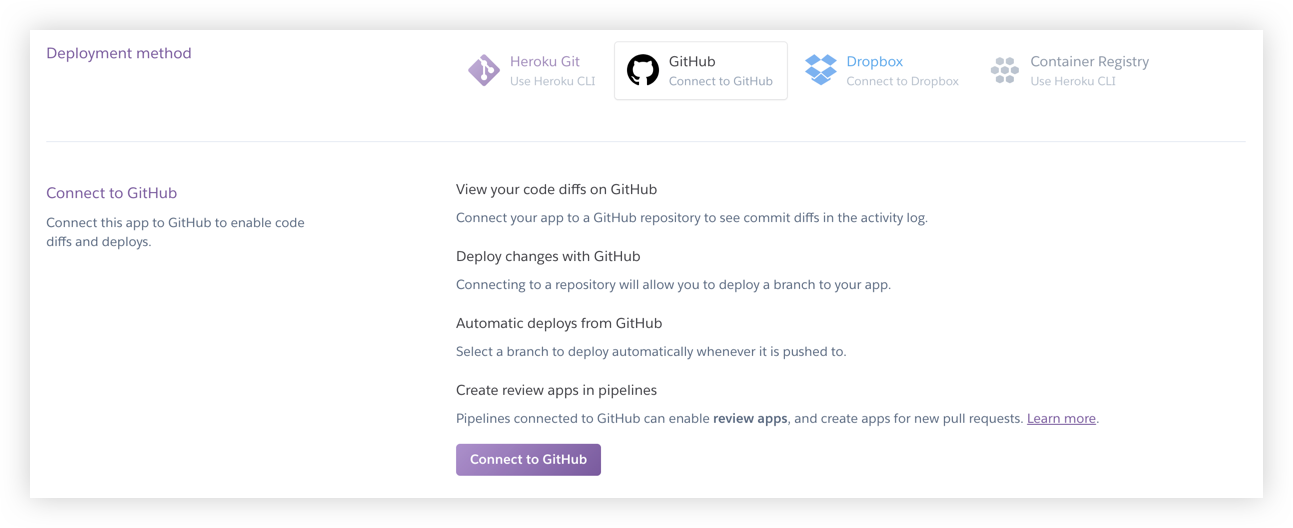
Heroku Deployment Methods
- We would also need a runner for the CD to run the job that checks the successful build of the codebase. GitLab provides shared runners for one repository for free!
How I won the scenario? 🏆
Ever wished for a deploy button? Pressing that would be fun!

the glorious deploy button
But in our system, we don’t even need that button to press. Here’s how:
1. Set up Heroku API Key
First, we will need an app on Heroku. If you don’t have an app yet, create one. The app name will be needed later.
Then, we will need to set up the API key so that it can connect to the runner.
- Go to dashboard.heroku.com/account to get the Heroku API Key.
- Place the Heroku API Key under Settings ➔ CI / CD ➔ Variables
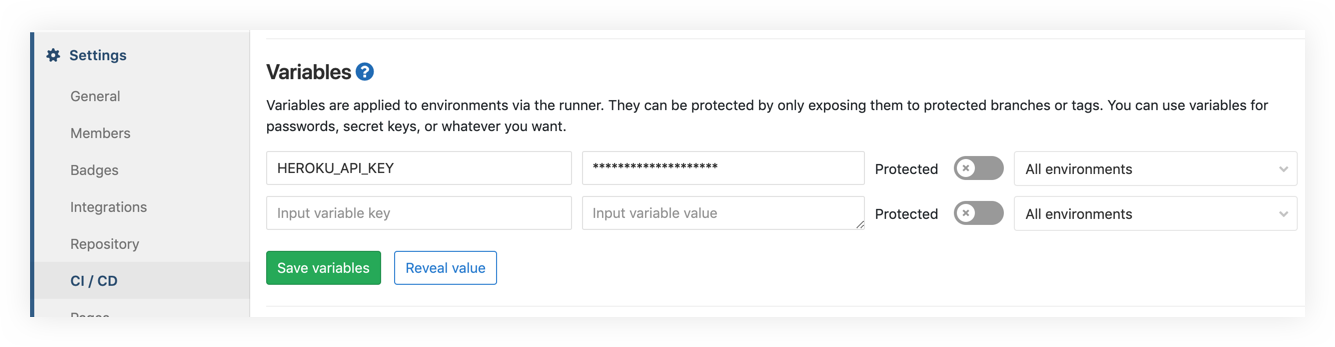
GitLab CI/CD Settings
We saved the key in a variable named HEROKU_API_KEY, we will use it later.
2. Write the GitLab deployment script
Now it’s time to write the .gitlab-ci.yml file.
My deployment script goes like this:
staging:
type: deploy
script:
- apt-get update -qy
- apt-get install -y ruby-dev
- gem install dpl
- dpl --provider=heroku --app=my_app --api-key=$HEROKU_API_KEY
only:
- master
As we can see, in the script section of the above snippet, we are installing ruby and a ruby gem called dpl. It’s a deploy tool made by Travis and can be used in GitLab as well. Then we are passing:
- provider name as heroku
--provider=heroku - the app name of our heroku app
--app=my_app - the api-key
--api-key=$HEROKU_API_KEYwhich we have saved earlier
Finally we are defining which branch changes should trigger the deployment.
3. Setup GitLab Runner
To run the pipeline we will need to install a runner (machine) which will run scripts and other programs to make sure our app is building successfully.
This doc explains how we can install the runner either on our local machine or in Docker: docs.gitlab.com/runner/install
4. Install Buildpack on Heroku (optional) for Meteor app
I’d recommend using the Meteor Buildpack Horse for Meteor app with Heroku which provides easy configuration to start the app. All we need to do is to define the ROOT_URL and MONGO_URL.
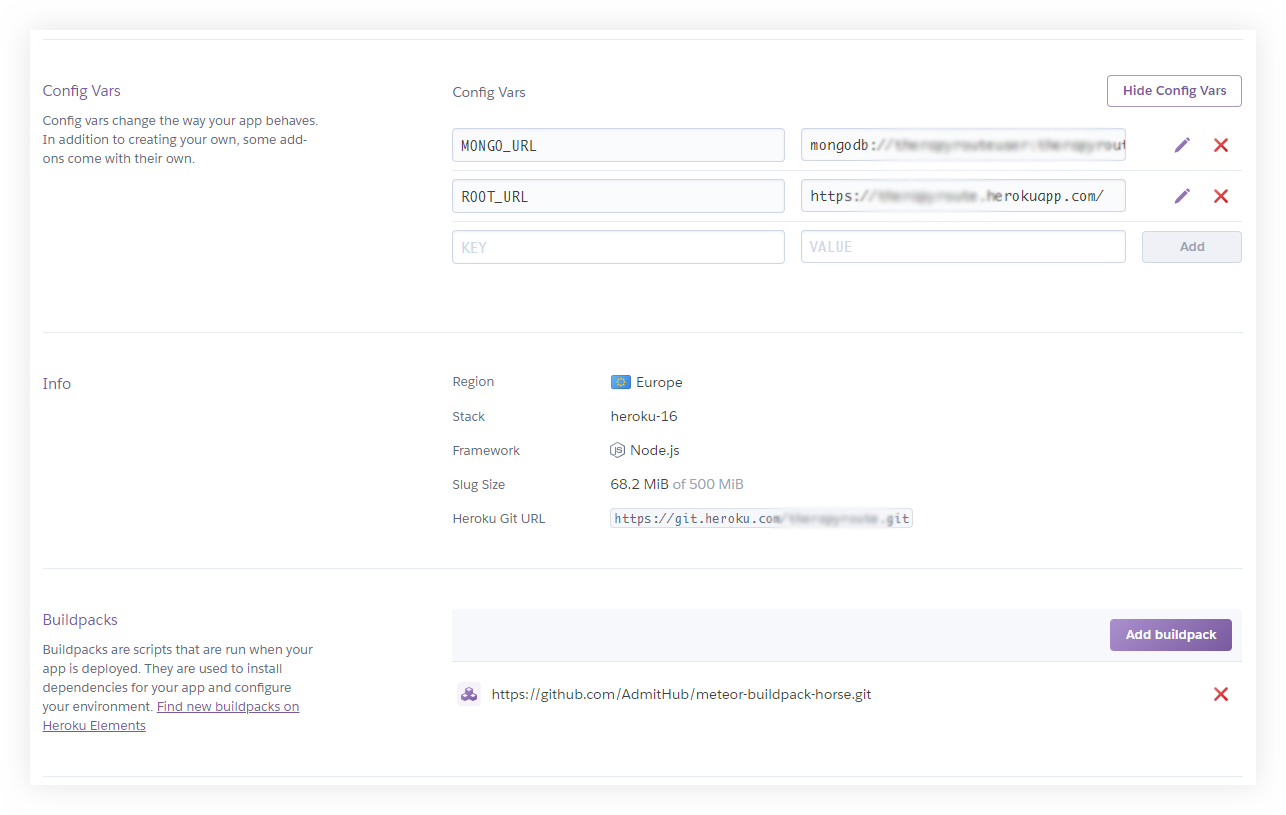
Heroku buildpack settings
And need to place the URL of this buildpack to Heroku, of course! Other available environment vars can be found here: github.com/AdmitHub/meteor-buildpack-horse#environment
I hope this short guide is helpful for beginners. Experts, please let me know suggestions and/or room for improvements if there’s any. Cheers!